Exploring the 10 Largest Banks in India in 2024
India is home to some of the largest and most influential banks, playing a critical role in shaping the country’s economy. With the rapid growth of financial services and technological advancements, Indian banks have expanded their reach, offering a wide range of products and services to meet the needs of individuals, businesses, and corporations.
These banks are not just limited to India; many have established a global presence, catering to the financial needs of clients across the world.
The banking sector in India is divided into public sector banks, private sector banks, and foreign banks. In this blog, we’ll explore the Largest Banks in India. Keep reading!
List of the Largest Banks in India
The following is the list of the Largest Banks in India.
- HDFC Bank
- ICICI Bank
- SBI
- Axis Bank
- Kotak Mahindra
- Bank of Baroda
- Punjab National Bank
- IndusInd Bank
- Indian Overseas Bank
- Canara Bank
1. HDFC Bank
HDFC Bank, one of India’s leading private sector banks, was founded in 1994. It began operations in Mumbai and quickly expanded its reach across the country. The bank’s foundation lies in providing efficient banking services with a focus on customer satisfaction. Today, HDFC Bank has over 6,500 branches and more than 18,000 ATMs spread across 2,900 cities in India.
The bank is renowned for its wide range of services, including personal banking, corporate banking, and loans such as home, auto, and personal loans. Additionally, HDFC Bank offers digital banking solutions, which make banking easier and more convenient for customers. Its mobile and internet banking platforms are user-friendly and feature a variety of services.
It is listed on major stock exchanges, both in India and internationally. The bank’s assets have grown to over ₹20 trillion (INR), making it one of the richest and most valuable banks in the country.
What sets HDFC Bank apart is its commitment to innovation and technology. It was one of the first banks in India to embrace digital banking, offering seamless online services to its customers.
You might also like: Richest Countries In Asia
2. ICICI Bank
ICICI Bank, founded in 1994, is one of the largest private sector banks in India. Headquartered in Mumbai, it has grown significantly over the years, with a network of over 5,400 branches and 15,000+ ATMs across India. The bank offers a variety of banking services such as savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment products. It also provides corporate banking services for businesses of all sizes.
ICICI Bank is known for its innovative use of technology, being among the first Indian banks to offer internet banking, mobile banking, and digital payment solutions. This makes banking convenient for its customers, allowing them to manage their accounts, transfer funds, and pay bills with ease.
With assets exceeding ₹15 trillion (INR), ICICI Bank is one of the wealthiest banks in the country. It is listed on both Indian and international stock exchanges, attracting investors worldwide due to its solid financial performance.
ICICI Bank has also expanded its international presence, with operations in 17 countries. The bank actively contributes to rural development, education, and health initiatives through its CSR programs.
3. SBI
The State Bank of India (SBI) is the largest and oldest public sector bank in India. It was founded in 1955 but traces its roots back to 1806 when the Bank of Calcutta was established. Headquartered in Mumbai, SBI has an extensive network of over 22,000 branches and 60,000 ATMs across the country, reaching even the most remote areas. Its presence also extends globally, with operations in over 30 countries.
It is a leader in retail loans, particularly in home loans and agricultural financing. Additionally, the bank provides robust digital banking platforms, offering internet banking, mobile banking, and YONO, a comprehensive digital app that simplifies everyday banking.
With assets surpassing ₹50 trillion (INR), SBI is the richest bank in India and ranks among the top banks in the world. It plays a critical role in India’s financial stability, contributing to national economic growth.
A unique aspect of SBI is its focus on rural banking. It has introduced several financial inclusion initiatives to provide banking access to the underserved and unbanked populations, ensuring affordable services for all.
4. Axis Bank
Axis Bank, founded in 1993, is one of India’s leading private sector banks. Headquartered in Mumbai, it has grown to become the third-largest private bank in India, with over 4,900 branches and more than 17,000 ATMs spread across the country. The bank serves millions of customers with a wide range of financial services.
Axis Bank is known for its focus on digital innovation, offering convenient and secure online banking services through its mobile apps and internet platforms. The bank also emphasizes personalized banking services for individuals and businesses, making it a popular choice for both retail and corporate clients.
With assets exceeding ₹13 trillion (INR), Axis Bank is a financially strong institution, listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange and the National Stock Exchange of India. Its consistent performance has earned it a reputation as a trustworthy bank.
The bank actively supports environmental and social initiatives through its Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) programs, focusing on education, financial literacy, and healthcare.
5. Kotak Mahindra
Kotak Mahindra Bank, established in 2003, is one of India’s leading private sector banks. It began as Kotak Mahindra Finance Ltd., a non-banking financial institution, before receiving a banking license from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Headquartered in Mumbai, Kotak Mahindra Bank has since grown to become a major player in India’s financial sector, with over 1,700 branches and more than 2,700 ATMs across the country.
It is known for its efficient digital banking platforms, allowing customers to access services like mobile banking, internet banking, and seamless digital payments with ease.
With assets totaling over ₹5 trillion (INR), Kotak Mahindra Bank is financially strong and has earned a reputation for steady growth. The bank is listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange and the National Stock Exchange of India, making it a popular choice for investors.
A unique aspect of Kotak Mahindra Bank is its personalized approach to wealth management and investment solutions. It offers tailored financial advice and services for high-net-worth individuals, making it a preferred bank for wealth management.
Also see: Strongest Currencies in the World
6. Bank of Baroda
Bank of Baroda (BoB) is one of India’s oldest and largest public sector banks, founded in 1908 by Maharaja Sayajirao Gaekwad III in the city of Baroda (now Vadodara). With its headquarters in Mumbai, the bank has expanded globally, operating in more than 20 countries with over 8,200 branches and 10,000+ ATMs worldwide.
BoB offers a broad range of financial services, including retail banking, corporate banking, loans, and international banking solutions. It serves millions of customers, providing various products such as savings accounts, fixed deposits, and credit cards, along with more specialized services like wealth management and insurance.
With assets totaling over ₹12 trillion (INR), Bank of Baroda is one of India’s most financially robust banks. It is listed on major stock exchanges, including the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE), reflecting its strong market presence.
What sets Bank of Baroda apart is its international reach and focus on providing banking services to a diverse range of clients, from individuals to large corporations. Additionally, the bank is committed to supporting India’s rural economy through its extensive rural banking network.
7. Punjab National Bank
Punjab National Bank (PNB), established in 1894, is one of India’s oldest and most respected public sector banks. Founded by Lala Lajpat Rai in Lahore, PNB played a significant role in the country’s financial history and growth. Today, the bank operates out of its headquarters in New Delhi and has a vast network of over 10,000 branches and 13,000+ ATMs across India, along with a presence in international markets.
PNB provides a wide array of banking services, including personal banking, corporate banking, loans, investment products, and digital banking solutions. It is known for catering to a diverse customer base, offering services to individuals, small businesses, and large corporations alike. PNB is also a leader in agricultural financing, supporting farmers with tailored loan schemes.
With assets exceeding ₹12 trillion (INR), PNB ranks among India’s most financially strong banks. It is listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange and the National Stock Exchange, with a long history of stable performance.
What distinguishes PNB is its emphasis on inclusive banking, ensuring that underserved and rural populations have access to financial services. The bank has also embraced digital transformation, offering mobile banking, internet banking, and other digital services to simplify banking for its customers.
8. IndusInd Bank
IndusInd Bank, established in 1994, is a prominent private sector bank in India. Headquartered in Mumbai, the bank was founded with a focus on providing modern banking services while catering to the evolving needs of customers. Over the years, IndusInd Bank has built a strong network of over 2,000 branches and 2,800+ ATMs across the country.
The bank offers a wide variety of services, including savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment products. It is also well-known for its corporate banking services, catering to businesses with tailored solutions such as cash management, trade finance, and lending options. Additionally, the bank places a significant focus on digital banking, offering seamless mobile and online banking platforms for easy transactions.
Financially robust, IndusInd Bank has assets exceeding ₹4 trillion (INR) and is listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE). It has consistently demonstrated strong financial performance, making it a popular choice for investors.
The bank has taken various initiatives to promote green banking and energy efficiency, which includes offering eco-friendly banking services and supporting community-based projects.
9. Indian Overseas Bank
Indian Overseas Bank (IOB) is a public sector bank in India, founded in 1937 by M. Ct. M. Chidambaram Chettyar with a vision to promote overseas banking and foreign exchange operations. Headquartered in Chennai, the bank has grown significantly and now operates a large network of over 3,200 branches and 3,300+ ATMs across India, with a notable presence internationally, particularly in Singapore, Colombo, and Bangkok.
The bank is particularly known for its focus on foreign exchange and overseas banking, providing specialized services to individuals and businesses involved in international trade. It also offers digital banking services, such as mobile and internet banking, enabling customers to manage their finances conveniently.
IOB offers a wide range of banking services, including personal banking, corporate banking, loans, and wealth management.
The bank’s assets stand at around ₹2.7 trillion (INR), making it a strong financial institution in India’s banking sector. IOB is listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE), reflecting its strong market position.
With its legacy in international banking and a commitment to modern digital solutions, Indian Overseas Bank continues to be a significant player in the Indian banking landscape.
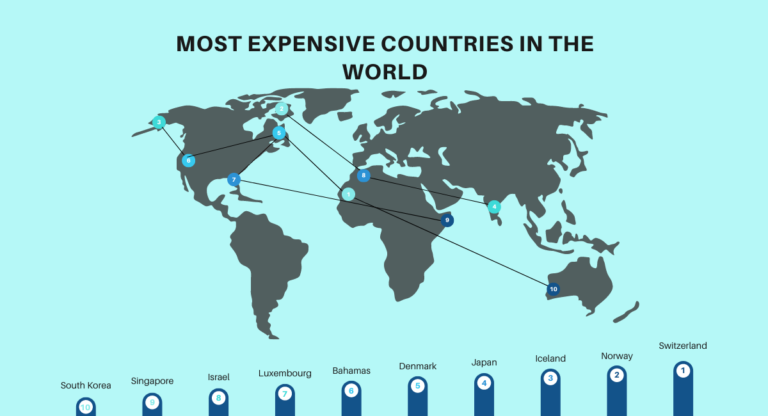
Also read: Most Expensive Countries in the World
10. Canara Bank
Canara Bank is one of India’s oldest and most prominent public sector banks. It was founded in 1906 by Ammembal Subba Rao Pai in Mangalore with a mission to provide financial services to people from all walks of life. Over the years, Canara Bank has grown significantly, expanding its network to over 9,700 branches and more than 12,000 ATMs across India, with a global presence in locations such as London, Dubai, and New York.
The bank offers a wide array of services, including savings and current accounts, loans, credit cards, investment products, and insurance. It is particularly known for its corporate banking services and has a strong focus on providing financial assistance to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Canara Bank has assets totaling over ₹13 trillion (INR), making it one of the richest and most stable banks in India. It is listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE), reinforcing its financial strength and market credibility.
A unique feature of Canara Bank is its emphasis on inclusive banking. The bank actively supports rural development through various financial inclusion initiatives, promoting affordable banking services in underserved regions. It is also known for its corporate social responsibility (CSR) efforts, focusing on education, healthcare, and environmental sustainability.
Here’s an informative table summarizing the largest banks in India, along with key details about each:
| Bank Name | Founded | Headquarters | Branches | ATMs | Assets (₹ Trillion) | Key Services | Notable Features |
| SBI | 1955 | Mumbai | 22,000 | 60,000 | 50 | Retail loans, agricultural financing, digital banking | Focus on rural banking and financial inclusion |
| HDFC Bank | 1994 | Mumbai | 6,500 | 18,000 | 20 | Personal banking, corporate banking, loans | Early adopter of digital banking |
| ICICI Bank | 1994 | Mumbai | 5,400 | 15,000 | 15 | Savings accounts, loans, credit cards, corporate banking | Pioneered internet and mobile banking |
| Canara Bank | 1906 | Mangalore | 9,700 | 12,000 | 13 | Savings accounts, loans, corporate banking | Strong focus on rural development |
| Axis Bank | 1993 | Mumbai | 4,900 | 17,000 | 13 | Retail and corporate banking, loans | Strong emphasis on digital innovation |
| Bank of Baroda | 1908 | Mumbai | 8,200 | 10,000 | 12 | Retail and corporate banking, wealth management | Strong international presence |
| Punjab National Bank | 1894 | New Delhi | 10,000 | 13,000 | 12 | Personal and corporate banking, agricultural loans | Emphasis on inclusive banking |
| Kotak Mahindra | 2003 | Mumbai | 1,700 | 2,700 | 5 | Digital banking, wealth management | Personalized wealth management services |
| IndusInd Bank | 1994 | Mumbai | 2,000 | 2,800 | 4 | Savings accounts, loans, corporate banking | Initiatives in green banking |
| Indian Overseas Bank | 1937 | Chennai | 3,200 | 3,300 | 2.7 | Personal banking, corporate banking, foreign exchange | Focus on overseas banking |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Largest Banks in India have become a vital part of the nation’s economic development, playing a significant role in providing financial services to millions of individuals and businesses. Public sector banks, with their vast branch networks and government support, ensure stability, while private sector banks drive innovation and customer satisfaction through advanced digital platforms. Together, they offer a comprehensive range of banking services, from personal savings accounts to complex corporate financing.
FAQs
What Is the Biggest Bank in Asia?
The biggest bank in Asia, in terms of total assets, is Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC). ICBC is also the largest bank in the world by assets. As of recent reports, ICBC holds assets exceeding $5 trillion (USD). The bank was established in 1984 and is headquartered in Beijing, China. It provides a wide range of financial services, including corporate banking, personal banking, investment services, and wealth management.
Who Funds the World Bank?
The World Bank is funded primarily by its member countries. The 189 member countries provide the financial resources that allow the World Bank to carry out its development and lending programs.
- Capital Contributions from Member Countries: Each member country contributes capital when they join the World Bank. The amount each country contributes is based on its economic size and financial capacity.
- Borrowing from International Markets: The World Bank raises most of its funds by issuing bonds in the global financial markets. These bonds are purchased by investors, and because the World Bank is backed by its member countries, it has a strong credit rating, allowing it to borrow at low interest rates.
Which Country Has the Highest Loan From the World Bank?
As of recent reports, India is the country with the highest cumulative loans from the World Bank. The World Bank provides loans and grants to countries for projects aimed at improving infrastructure, reducing poverty, and fostering economic development. India, as a developing country with a large population and significant infrastructure needs, has been one of the largest recipients of World Bank assistance for many years.
Who Is the President of the World Bank?
Ajay Banga is serving as the President of the World Bank. He succeeded David Malpass and is the 14th president of the institution.
Ajay Banga, an Indian-American business leader, was formerly the CEO of Mastercard. The President of the World Bank plays a crucial role in guiding the bank’s policies, operations, and strategic vision for international development.
Who Runs the IMF?
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is headed by a Managing Director, who is the chief executive of the organization. The Managing Director of the IMF is Kristalina Georgieva. She is a Bulgarian economist and the first person from an emerging market economy to lead the IMF.

I’m Sophia Jones, an adventurer at heart from New York City, USA. I live for travel and exploration, always eager to discover new places, meet fascinating people, and try out diverse cuisines. Over the past few years, I’ve traveled to numerous countries, immersing myself in different cultures and creating unforgettable memories.